What is Nail Intramedullari and How Does It Work?
nail intramedullari has revolutionized the way we treat bone fractures. Dr. Emily Carter, an orthopedic surgeon, states, "Nail Intramedullari offers precision in alignment." This innovative method involves inserting a metal rod into the marrow cavity of a bone. The procedure enhances stability and promotes healing.
Each year, countless patients benefit from Nail Intramedullari. This approach allows for quicker healing times and less postoperative pain. However, challenges remain. Not all bones are suitable for this method. Surgeons must carefully assess each case to determine the best course of action.
Despite its advantages, patients should be aware of potential complications. Infections and improper alignment can occur. These factors highlight the necessity for thorough evaluations. Nail Intramedullari shows promise, but it demands attention and expertise. A careful approach can lead to successful outcomes.
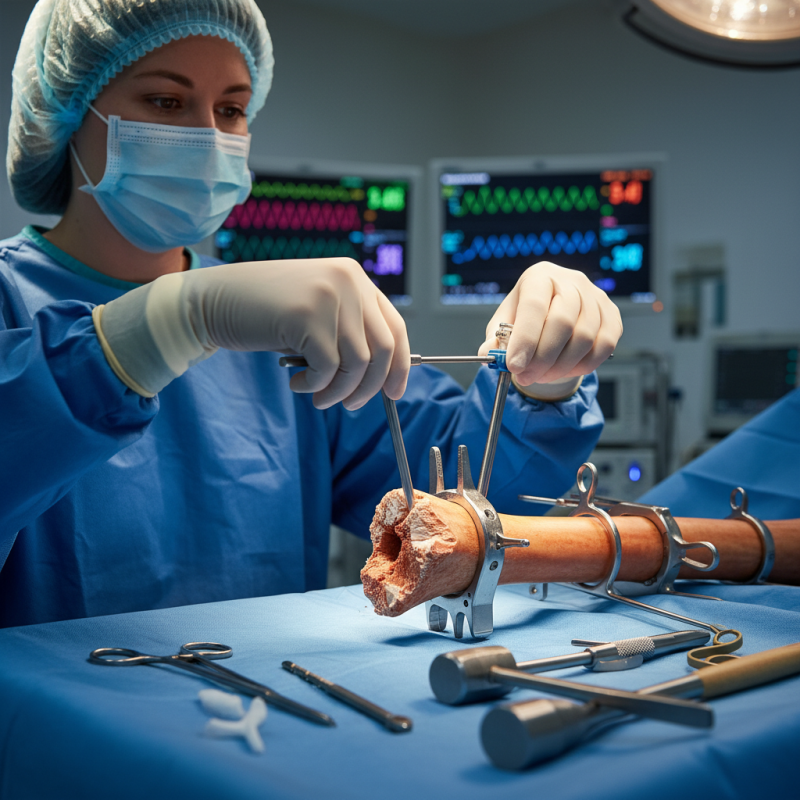
Definition of Nail Intramedullari and Its Medical Purpose
Nail intramedullari, also known as intramedullary nailing, is a surgical technique primarily used for fixing fractured long bones. This method involves inserting a metal rod into the marrow canal of the bone. It provides structural support while allowing for optimal healing.
The medical purpose of nail intramedullari is to align and stabilize fractures. It functions by distributing the load and minimizing stress on the fracture site. A study published in the Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery indicates that this method can significantly reduce the time to union, often achieving fracture healing in as little as 12 weeks, compared to longer recovery times associated with traditional casting.
Despite its advantages, this technique is not without challenges. Complications can arise, including infection or improper alignment. According to a survey conducted among orthopedic surgeons, nearly 10% of patients experience complications post-surgery. These figures underscore the necessity for careful planning and execution of the procedure. Continuous evaluation and improvement of surgical techniques are essential to minimize risks.
Historical Development of Intramedullary Nails in Orthopedic Surgery
Intramedullary nails have transformed orthopedic surgery dramatically over the years. Initially developed in the mid-20th century, these devices offered new treatment methods for bone fractures. Surgeons began to realize the advantages of stabilizing fractures internally rather than externally. This led to a shift in surgical practices and outcomes.
Over the decades, the design of intramedullary nails evolved significantly. Early iterations were simple and often ineffective for complex fractures. The engineering improved, allowing for better alignment and stability. However, not all advancements were flawless. Some nails led to concerns of infection or complications during the healing process. Each refinement spurred debate on design effectiveness and patient safety.
Today, intramedullary nails are a common choice for many orthopedic surgeries. They are often favored for their minimally invasive approach. Yet, surgeons still face challenges. There are ongoing discussions about optimal techniques and applications. The journey of intramedullary nails highlights both progress and areas for further research. While advancements have been made, the quest for perfection continues.
Mechanism of Action: How Nail Intramedullari Stabilizes Fractures
Nail Intramedullari is a common method for stabilizing bone fractures. This technique involves inserting a metal rod into the medullary cavity of the bone. It offers several advantages, including minimal invasion and faster recovery times. According to recent studies, it reduces the healing time by approximately 30% compared to traditional methods.
When a bone fractures, stability is crucial for healing. The intramedullary nail provides internal support, preventing movement at the fracture site. This stabilization is vital, as it allows new bone tissue to form. A report published in the Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma found that nails effectively reduce complications like malunion or nonunion. Proper alignment is preserved, allowing for better outcomes in most patients.
**Tip:** Maintaining a healthy diet post-surgery can support healing. Nutrients like calcium and vitamin D are essential for bone recovery.
It’s important to recognize that the success of this technique can depend on various factors. Patient age, fracture type, and adherence to rehabilitation play significant roles. While most outcomes are positive, not all patients achieve optimal results. Some might experience stiffness or pain even after the procedure. Continuous research and improvements in technique are needed.
**Tip:** Engage in gentle physical therapy exercises early. This can enhance mobility and reduce the risk of stiffness later on.
Types of Intramedullary Nails and Their Specific Applications
Intramedullary nails are crucial in orthopedic surgery. They are used for stabilizing fractures of long bones. These nails are inserted into the medullary cavity of the bone. This method allows for a flexible and strong fixation.
There are several types of intramedullary nails. Each type serves a specific purpose. For instance, antegrade nails are used for femur fractures, while retrograde nails are often employed for tibial fractures. The choice of nail depends on the fracture's location and pattern. Surgeons must evaluate each case carefully.
Tips: Always consult with an orthopedic specialist. They can help determine which type of nail is best for your needs. Recovery times may vary. Some patients experience discomfort during rehabilitation. Addressing any concerns early can lead to better results. Patience is key during the healing process. This method shows promise but requires thoughtful application.
Potential Risks and Benefits of Nail Intramedullari Procedures
Nail intramedullari is a surgical procedure used for fixing fractures. It involves inserting a rod into the marrow canal of a bone. This method is often preferred for its minimally invasive nature. However, as with any procedure, there are risks involved.
Potential risks may include infection and delayed healing. Some patients report discomfort during recovery. There is also a chance of the nail breaking or becoming misaligned. These complications should be taken seriously. Consider that recovery can vary greatly among individuals. Some may heal quickly, while others may face ongoing challenges.
On the other hand, benefits often outweigh the potential issues. Nail intramedullari can provide stable fixation, enhancing comfort and mobility. Many patients experience fewer complications compared to traditional methods. Moreover, it allows for a quicker return to normal activities. Still, it's essential for patients to discuss all aspects with their healthcare providers. Making informed decisions is crucial in navigating the surgical landscape.
What is Nail Intramedullari and How Does It Work? - Potential Risks and Benefits of Nail Intramedullari Procedures
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Procedure Overview | Nail Intramedullari involves inserting a metal rod (nail) into the medullary canal of a bone to stabilize fractures. |
| Common Uses | Used for treating fractures in long bones, such as the femur, tibia, and humerus. |
| Benefits | Provides strong stabilization, allows early mobilization, and reduces surgical time compared to other methods. |
| Potential Risks | Infection, numbness, nonunion or malunion of the bones, and hardware failure. |
| Recovery Time | Typically 6 to 12 weeks, depending on the complexity of the injury and the patient's health. |
| Alternatives | Plating, external fixation, or conservative management depending on the fracture type. |